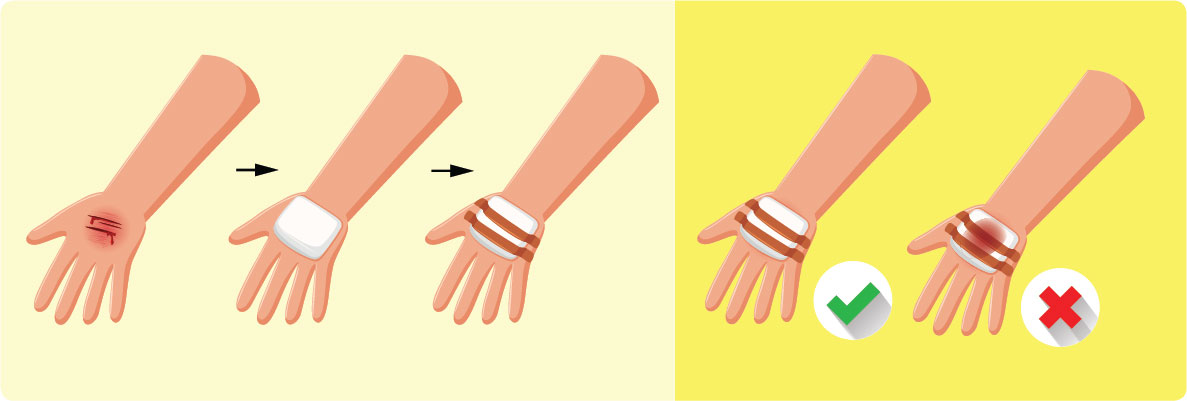
A wound is an injury to the skin that “breaks” the barrier to the environment. The skin protects the internal organs of the body from the environment. When the skin is damaged or injured, the wound can bleed or become infected.
Wound healing occurs after an injury and there are many stages to which healing takes place. It is important to note that: