Breast cancer is the number one cancer among Singaporean women. It usually occurs when harmful (malignant) cells originate from the cells lining the milk ducts and glands. In advanced breast cancer, cancerous cells can spread through the breast to the rest of the body.
According to the Singapore Cancer Society, 1850 women are diagnosed with breast cancer every year and more than 400 would die from the disease. Advancements in breast cancer screening allow healthcare professionals to diagnose breast cancer earlier. Finding the cancer earlier makes it much more likely that the cancer can be cured.
There are five stages of breast cancer that are commonly expressed as numbers on a scale of 0 through IV. They can be categorized into three types: non-invasive, invasive and metastatic.
Stage 0
Stage 0 refers to non-invasive breast cancer such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) that is confined to the ducts. This means that cancerous or non-cancerous cells are localized and did not break out into neighboring breast tissues.
Stage I
Stage I breast cancer is invasive, which means that cancer cells have developed and spread to surrounding breast tissues.
Stage II
Stage II breast cancer is divided into subcategories - IIA and IIB.
IIA refers to invasive breast cancer where no tumor is located but cancer cells (larger than 2 mm) is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes under the arm or near the breast bone.
IIB refers to invasive breast cancer where the tumor is between 2-5 cm with small groups of cancer cells found in the lymph nodes. In some cases, the tumor can be larger than 5 cm but may not have spread to the axillary lymph nodes.
Stage III
Stage III breast cancer is divided into subcategories - IIA, IIB and IIC.
Stage IV
Stage IV breast cancer, also known as metastatic breast cancer, refers to invasive breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and lymph nodes to other parts of the body such as the lungs, bones or brain.
Signs and symptoms of Breast Cancer may include:
Biopsy
A breast biopsy is done to determine the presence of breast cancer.
Mammogram
Mammogram is a screening tool that can detect the presence of lumps and growths in the breast. During the screening, a technologist will place the woman's breast on a plate while another plate will be used to press the breast from above; flattening and holding it still while the X-ray is taken.
Women above 40 are advised to go for mammogram once a year. However, those who present with a family history and/or other underlying health conditions may need to consult with their physician for other required measures.
Breast Self-examination
Women above 20 are strongly encouraged to perform Breast Self-examination (BSE) monthly to check for any abnormal lumps or growths. BSE could be done in the shower or when lying down, before one retires for the night.
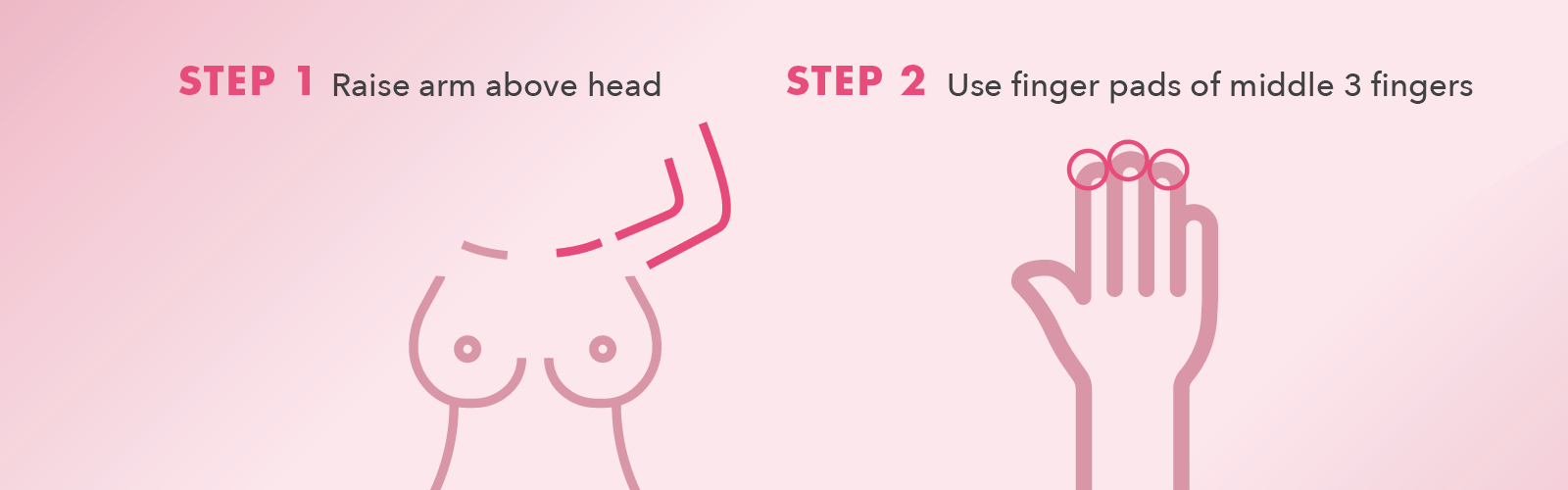
Here's how to perform a BSE:
.2020-10-11-01-30-19.jpg)
.2020-10-11-01-31-05.jpg)


