Slipped Disc
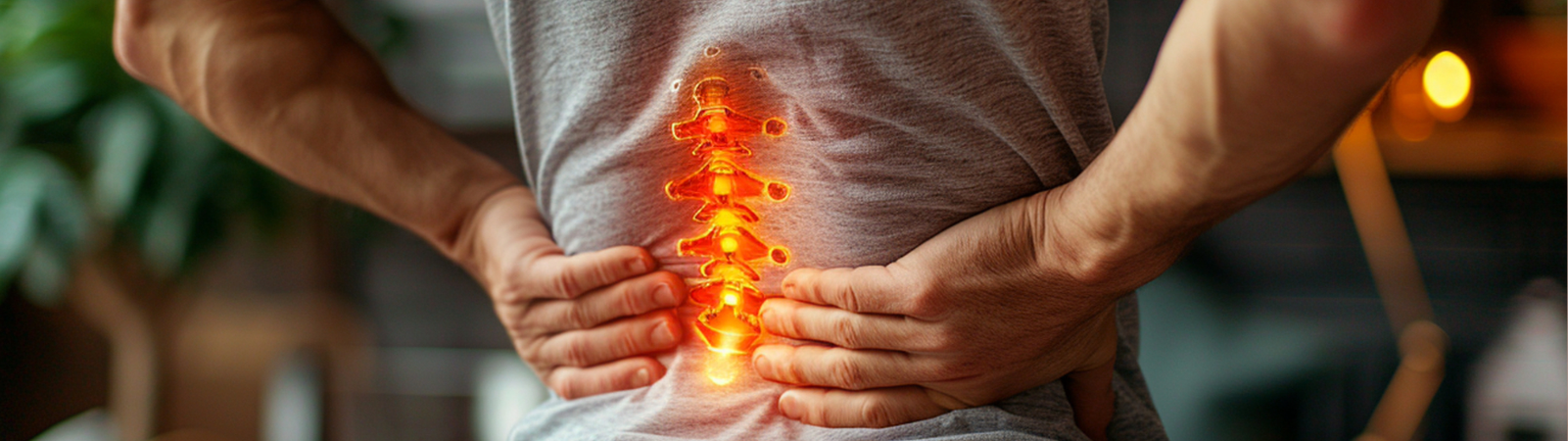
What is a Slipped Disc?
A slipped disc, or herniated disc, happens when there is a tear in the outer covering of the discs in your vertebra, resulting in the internal gel filling being pushed out of the covering and press on the nerve root. A slipped disc is also called a herniated disc or a ruptured disc.
A slipped disc can occur in any part of the spine, most often in the lower back and depending on where the slipped disc is located, it may result in pain, numbness or weakness in an arm or a leg.
Some symptoms you may experience include:
- Lower back pain
- Numbness or tingling in your shoulders, back, arms, hands, legs or feet
- Neck pain
- Problems bending or straightening your back
- Muscle weakness
- Pain in the buttocks, hips or legs
Risk Factors for Slipped Discs
- Being overweight: Excess body weight may put extra stress on the discs in your lower back.
- Occupational risks: If you are in a physically demanding job, you’ll have a greater risk of back problems. Repetitive lifting, pulling, pushing or bending over may also increase your risk.
- Genetics: Some people have a genetic disposition to developing slipped disc due to family history.
- Smoking: Cigarettes contain nicotine and other toxins that prevent nutrients from being absorbed by the discs which accelerates disc degeneration.
- Lack of exercise: Regular exercise lowers your risk of slipped discs by strengthening the core muscles that support the spine.
Preventing a Slipped Disc
Some ways you can prevent a slipped disc include:
- Exercising to strengthen your core muscles that support the spine.
- Maintain a good posture to reduce pressure on your spine and discs. Keep your back straight and aligned when sitting and bend your knees and hips when lifting heavy objects instead of bending forward.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce extra pressure on your spine and discs.
- Quit smoking to keep your discs from drying out due to the toxins from cigarettes.
Bracing Through the Pain
After years of suffering from debilitating back pains, Mr. Adrian Yeo was diagnosed with scoliosis and spondylolisthesis. Read more about his history and journey to recovery with orthopedic surgeon Dr. Mash here.
Read the story
Understanding Bone & Joint Care: Your Guide to Diagnosis, Treatment, and Support
Move well. Feel well. Caring together for your bones and joints means taking care of your range of movements and the quality of life you want. From exercise and nutrition, to attending to injuries and long- and short-term conditions, moving well can influence your daily routines, work and play.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
This resource provides information about cancer, including:
- Importance of Bone & Joint Care: Understand the importance of maintaining your bone and joint health.
- Common Orthopedic Conditions: Learn about the different types of common orthopedic conditions and their characteristics.
- Key Risk Factors: Explore various modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors that may leave you susceptible to orthopedic conditions.
- Ways to Improve Bone & Joint Care: Learn about lifestyle factors and preventive measures to minimize your risk of orthopedic conditions.
What is Bone & Joint Care?
Bone and joint care focuses on maintaining the health and function of your musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It involves preventing, diagnosing, and treating conditions that affect these structures, such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, fractures, sprains, and strains. Good bone and joint health is essential for mobility, independence, and overall quality of life.
Importance of Bone & Joint Care
- Mobility & independence: Healthy bones and joints allow you to move freely and perform daily activities without pain or limitations.
- Pain prevention: Bone and joint problems can cause chronic pain that affects your ability to work, sleep, and enjoy life.
What Causes Orthopedic Conditions?
Heart disease is caused by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Non-Modifiable Factors: Age, gender, ethnicity family history, and inherited genetic mutations.
- Modifiable Factors:
- Lifestyle: Diet, occupation, sports and physical activities, and poor posture.
- Health: Obesity, Prior injuries
Symptoms of Orthopedic Conditions
Symptoms of orthopedic conditions may vary depending on the type of orthopedic conditions. However, some general signs and symptoms include:
- Pain in the affected segment of the bone or joint
- Swelling and Redness
- Joint stiffness
- Limited range of movement
- Numbness, tingling or weakness
Important Note: These symptoms may also be indicative of other health conditions. Speak to our Specialists today for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Common Orthopedic Conditions in Singapore
- Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes the breakdown of cartilage, the smooth tissue that cushions the ends of bones in joints.
- Fractures happen when there is a break in a bone, which can be caused by trauma or osteoporosis.
- Sprains & Strains, are stretches or tears of a ligament (sprain) and stretches or tears of a muscle or tendon (strain).
- Back Pain can be caused by various factors, including muscle strains, ligament sprains, disc herniation, and spinal stenosis.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome happen when the median nerve, which runs through the wrist, is compressed.
- Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that typically develops during adolescence.
Orthopedic Treatment Goals
- Relieve pain to reduce discomfort and improve daily functioning
- Restore and maintain function to help patients return to normal activities
- Slow disease progression, especially in chronic conditions
Improving Bone & Joint Health
Here are some helpful ways to improve your bone & joint health:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with an emphasis on calcium-rich food such as dairy-products and leafy green vegetables.
- Get enough vitamin D which is essential for calcium absorption. You can do so by getting sufficient sunlight or from fortified foods and supplements.
- Engage in regular physical activities by doing weight-bearing exercises such as jogging or stair climbing, muscle-strengthening exercises which build muscle mass and flexibility exercises such as yoga and stretching.
- Practice good posture, avoid slouching and maintain proper posture while sitting and standing.
- Manage existing medical conditions such as arthritis and osteoporosis through medication and lifestyle changes.

